Food webs energy pyramids and an introduction to biodiversity – Food webs, energy pyramids, and biodiversity are interconnected concepts that play a crucial role in the functioning of ecosystems. This introduction provides an overview of these topics, exploring their definitions, importance, and relationships.
Food webs are complex networks of interconnected organisms that depict the feeding relationships within an ecosystem. Energy pyramids illustrate the flow of energy through trophic levels, while biodiversity encompasses the variety of life forms and their interactions.
Introduction to Food Webs

Food webs are intricate networks of interconnected food chains within an ecosystem. They depict the feeding relationships between different species and illustrate the flow of energy and nutrients through the system. Understanding food webs is crucial for comprehending ecosystem dynamics, species interactions, and the overall stability of natural communities.
Within a food web, organisms are categorized into trophic levels based on their feeding habits:
- Producers (Autotrophs):Organisms that produce their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis.
- Primary Consumers (Herbivores):Organisms that feed directly on producers.
- Secondary Consumers (Carnivores):Organisms that feed on primary consumers.
- Tertiary Consumers (Top Predators):Organisms that feed on secondary consumers.
Food webs vary in complexity, ranging from simple linear chains to complex interconnected networks. They are found in all ecosystems, from terrestrial forests to aquatic environments.
Energy Pyramids
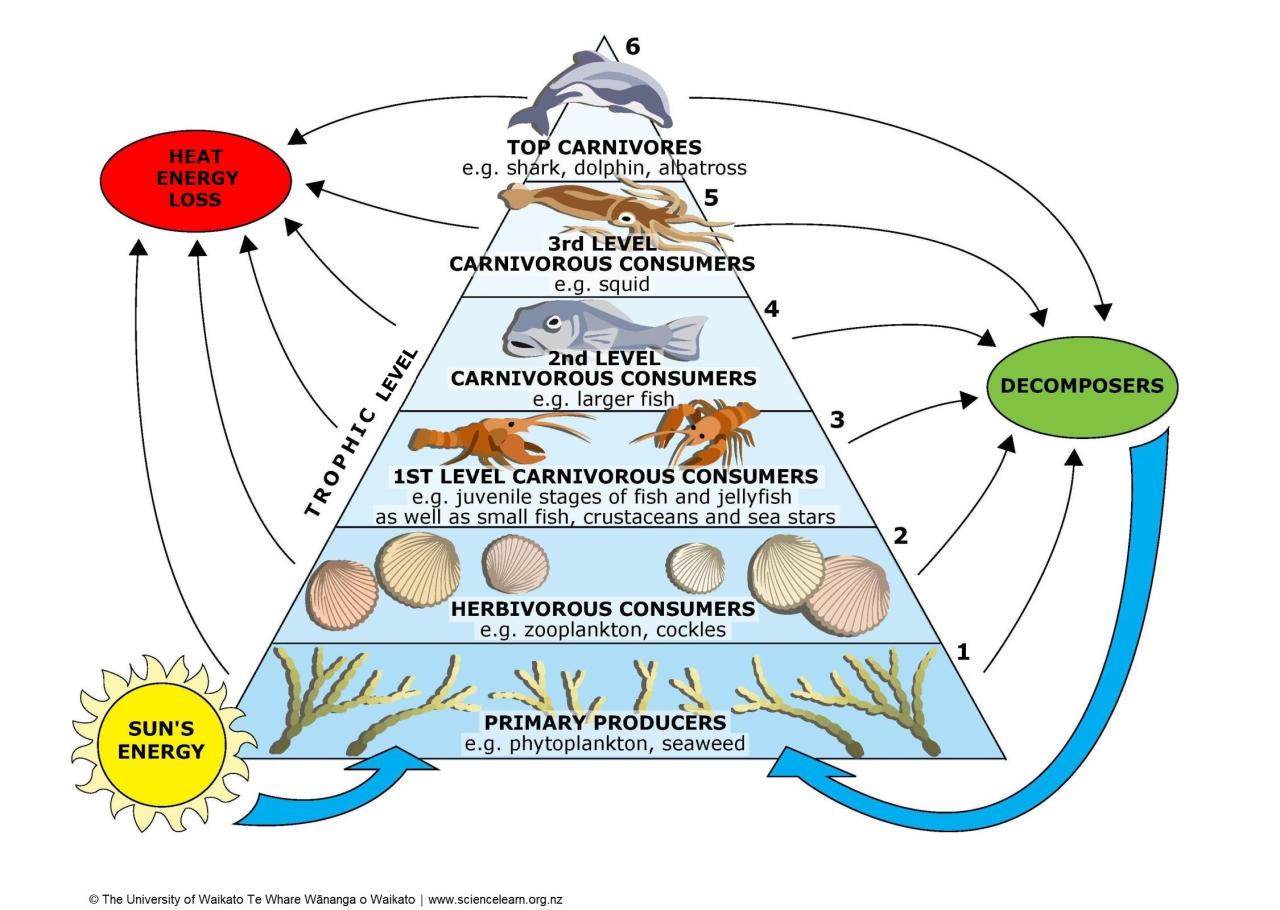
Energy pyramids are graphical representations of the energy flow within a food web. They depict the amount of energy available at each trophic level, with producers forming the base and top predators occupying the apex.
There are different types of energy pyramids:
- Biomass Pyramids:Represent the total mass of organisms at each trophic level.
- Production Pyramids:Represent the rate at which energy is produced at each trophic level.
Energy pyramids demonstrate the inefficiency of energy transfer between trophic levels, with only a small fraction of energy passing from one level to the next. This inefficiency limits the number of trophic levels that can be supported within an ecosystem.
Biodiversity: Food Webs Energy Pyramids And An Introduction To Biodiversity

Biodiversity refers to the variety of life forms within an ecosystem, encompassing the genetic diversity within species, the diversity of species, and the diversity of ecosystems. It is a measure of the health and stability of an ecosystem.
There are different measures of biodiversity:
- Species Richness:The number of different species in an ecosystem.
- Species Diversity:The relative abundance of different species in an ecosystem.
Biodiversity is influenced by various factors, including climate, habitat availability, competition, and human activities.
Interconnections between Food Webs, Energy Pyramids, and Biodiversity

Food webs, energy pyramids, and biodiversity are interconnected and interdependent. Food webs provide the framework for energy flow and nutrient cycling, while biodiversity influences the stability and resilience of food webs. Energy pyramids help assess the health and productivity of ecosystems, which in turn affects biodiversity.
Maintaining biodiversity is crucial for the stability of food webs and energy flow. Diverse ecosystems are more resilient to disturbances and can better adapt to environmental changes. Conversely, disruptions to food webs or energy flow can have cascading effects on biodiversity.
Detailed FAQs
What is the significance of food webs?
Food webs reveal the intricate feeding relationships within ecosystems, showcasing the interdependence of organisms and the flow of energy and nutrients.
How do energy pyramids represent the flow of energy?
Energy pyramids depict the transfer of energy from producers to consumers, highlighting the loss of energy at each trophic level and the importance of efficient energy utilization.
What factors influence biodiversity?
Biodiversity is influenced by a multitude of factors, including habitat diversity, environmental conditions, species interactions, and human activities.