Bronsted lowry acids and bases worksheet – Embarking on the realm of Bronsted-Lowry acids and bases, this worksheet delves into the intricacies of this fundamental chemical concept, providing a comprehensive understanding of their properties, reactions, and applications. Dive into the world of proton transfer and explore the fascinating dynamics of acid-base chemistry.
Unveiling the characteristics of Bronsted-Lowry acids and bases, this guide elucidates their distinct properties, showcasing their ability to donate and accept protons. Delve into the mechanisms of acid-base reactions, unraveling the role of conjugate acid-base pairs and witnessing the transfer of protons firsthand.
Bronsted-Lowry Acids: Bronsted Lowry Acids And Bases Worksheet
Bronsted-Lowry acids are substances that donate protons (H+ ions) in a chemical reaction.
They have the following properties:
- They have a sour taste.
- They turn blue litmus paper red.
- They react with bases to form salts and water.
Some common examples of Bronsted-Lowry acids include:
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
- Sulfuric acid (H2SO4)
- Nitric acid (HNO3)
Bronsted-Lowry Bases
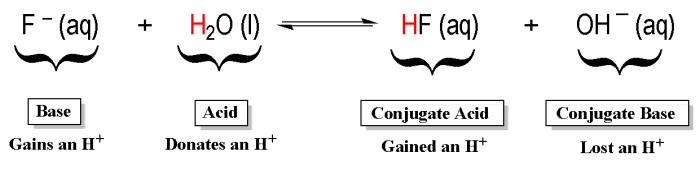
Bronsted-Lowry bases are substances that accept protons (H+ ions) in a chemical reaction.
They have the following properties:
- They have a bitter taste.
- They turn red litmus paper blue.
- They react with acids to form salts and water.
Some common examples of Bronsted-Lowry bases include:
- Sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
- Potassium hydroxide (KOH)
- Calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2)
Acid-Base Reactions
The Bronsted-Lowry theory of acid-base reactions states that an acid is a substance that donates a proton, and a base is a substance that accepts a proton.
In an acid-base reaction, the acid and base react to form a salt and water.
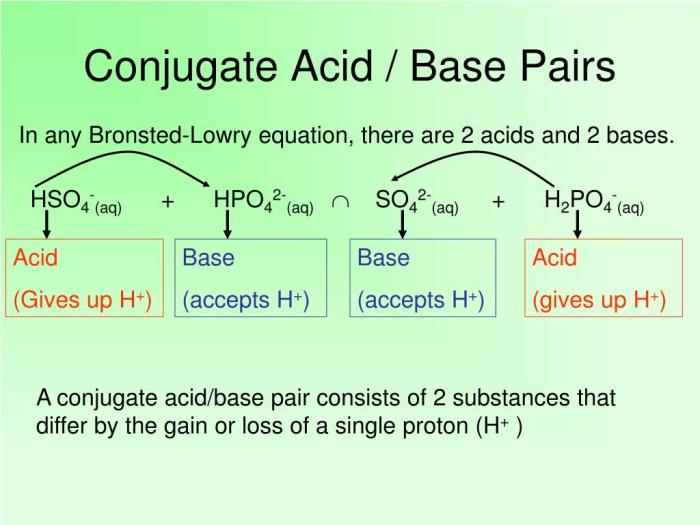
The conjugate acid-base pair is the acid and base that are formed when a proton is transferred.
For example, the conjugate acid-base pair for the reaction of hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide is hydrochloric acid (H+) and hydroxide ion (OH-).
Applications of Bronsted-Lowry Theory

The Bronsted-Lowry theory is used in a variety of fields, including chemistry, biology, and medicine.
In chemistry, the Bronsted-Lowry theory is used to understand acid-base equilibria.
In biology, the Bronsted-Lowry theory is used to understand the role of acids and bases in biological systems.
In medicine, the Bronsted-Lowry theory is used to understand the effects of acids and bases on the human body.
Questions Often Asked
What is the key difference between Bronsted-Lowry acids and bases?
Bronsted-Lowry acids donate protons, while Bronsted-Lowry bases accept protons.
Can water act as both an acid and a base?
Yes, water can undergo autoionization, acting as both a proton donor and a proton acceptor.
What is the role of conjugate acid-base pairs in acid-base reactions?
Conjugate acid-base pairs are formed when an acid donates a proton, creating its conjugate base, and a base accepts a proton, forming its conjugate acid.

