A laser emits a narrow beam of light, a unique and powerful tool with diverse applications. This concentrated beam of light, characterized by its coherence, monochromaticity, and directionality, has revolutionized fields ranging from manufacturing to medicine.
The properties of laser light, its beam characteristics, and its wide-ranging applications will be explored in this comprehensive discussion. By delving into the science behind laser technology, we gain insights into its remarkable capabilities and potential.
Definition of Laser
A laser (Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation) is a device that emits a narrow, concentrated beam of coherent light. This beam is characterized by its high intensity, directionality, and monochromaticity, which makes it a powerful tool in various fields.
Lasers find applications in numerous industries, including telecommunications, manufacturing, medical procedures, scientific research, and entertainment.
Properties of Laser Light
Laser light possesses unique properties that distinguish it from other light sources:
- Coherence:Laser light waves are in phase and synchronized, resulting in a highly focused beam.
- Monochromaticity:Laser light emits a very narrow range of wavelengths, producing a pure color.
- Directionality:Laser beams propagate in a highly concentrated, narrow path, minimizing divergence.
These properties contribute to the narrow beam emission of lasers, enabling precise control and focusing.
Laser Beam Characteristics
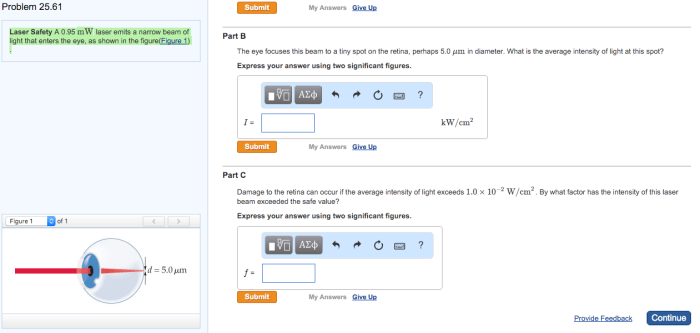
The beam width, divergence, and intensity of a laser beam are influenced by factors such as:
- Wavelength:Shorter wavelengths result in narrower beams.
- Output power:Higher power lasers produce more intense beams.
- Beam shaping optics:Lenses and mirrors can be used to manipulate the beam shape and characteristics.
Understanding these characteristics is crucial for optimizing laser performance in different applications.
Applications of Narrow Laser Beams
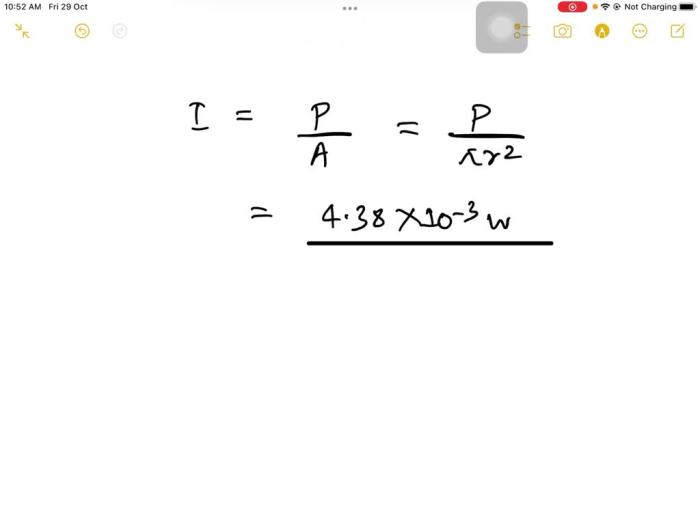
The narrow beam of a laser is essential in applications where precision and efficiency are paramount:
- Laser cutting:High-power lasers can precisely cut materials with minimal heat-affected zones.
- Optical communications:Laser beams are used in fiber optic cables to transmit data over long distances.
- Medical procedures:Lasers are employed in surgeries and therapies due to their ability to target specific areas with precision.
The narrow beam ensures accuracy, reduces damage to surrounding tissues, and enhances overall performance.
Comparison with Other Light Sources: A Laser Emits A Narrow Beam Of Light
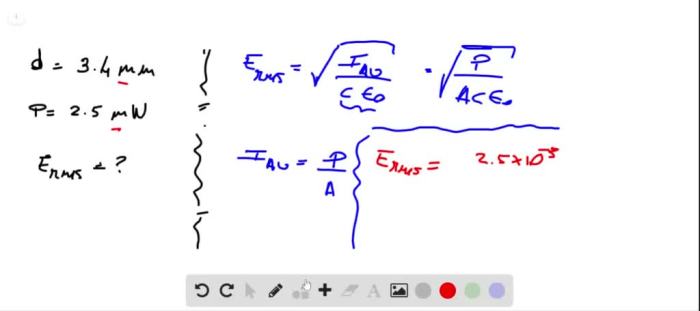
Laser light differs significantly from other light sources, such as incandescent bulbs or LEDs:
| Property | Laser | Incandescent Bulb | LED |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coherence | High | Low | Low |
| Monocromativity | High | Low | Moderate |
| Directionality | High | Low | Moderate |
| Beam Width | Narrow | Wide | Narrower than Incandescent |
| Applications | Precision cutting, optical communications, medical procedures | Lighting | Lighting, display screens |
These differences highlight the unique capabilities of lasers in applications requiring high precision and control.
Clarifying Questions
What is the difference between a laser and other light sources?
Lasers emit highly focused and coherent beams of light, while other sources like incandescent bulbs emit incoherent and dispersed light.
How does the narrow beam of a laser contribute to its applications?
The narrow beam allows for precise targeting, increased intensity, and efficient energy delivery, making it ideal for applications such as laser cutting, optical communications, and medical procedures.